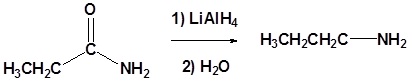(i) Reaction with sodium hydroxide
Acid chlorides react with NaOH to form the corresponding carboxylic acid which reacts with excess NaOH to form its sodium salt.
Mechanism of the reaction
(ii) Reaction with water
Acid chlorides also react with water by a similar mechanism to form the corresponding carboxylic acid.
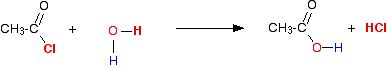
(iii) Reaction with alcohols
Acid chlorides react with alcohols to form esters
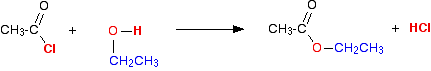
(iv) Reaction with phenol
Acid chlorides react with phenol to form phenyl esters.
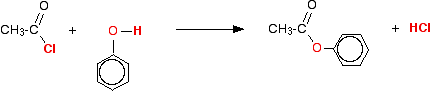
(v) Reaction with NH3
Acid chlorides react with ammonia to form amides
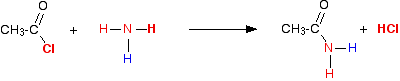
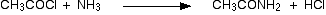
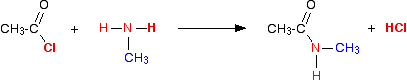
(vi) Reaction with primary amines
Acidchlorides react with amines to form alkyl amines.
(i) Esters undergo hydrolysis with dilute acids to form the corresponding carboxylic acid and the alcohol.
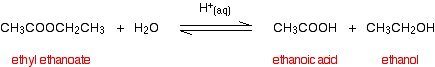
(ii) Esters when reacted with aqueous NaOH form the sodium salt of corresponding carboxylic acid and the alcohol.
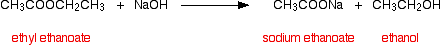
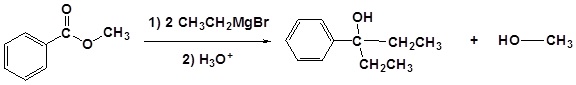
(iii) With Grignard reagent
Esters react with Grignard reagents to give tertiary alcohols. Here, the ester is first converted to a ketone which reacts rapidly with the Grignard reagent again to give the product.
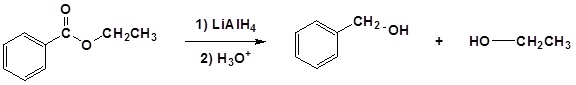
(iv) Reduction by LiAlH4

(i) With NaOH
When amides are warmed with an aqueous solution of NaOH, NH3 is liberated and the sodium salt of the corresponding carboxylic acid is formed.

(ii) With LiAlH4
Amides are reduced to the corresponding primary amine with LiAlH4