chemical bond – The electrons in the valence shell of the atom are involved in the formation of bonds. The attraction present between the atoms so as to minimize the energy in a polyatomic system is called a chemical bond.
Ionic bonds
• The electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions that are formed when the valence electrons of one atom are given to another atom during the formation of a bond between a pair of atoms with a high difference in electronegativity, is called the ionic bond.
• When sodium chloride in the solid state is considered, the ions are attracted electrostatically and packed in a definite pattern. Therefore, when an ionic compound exists in the solid state, ions do not have the ability for movement. Particles can only vibrate while being in the places where they are situated. Accordingly, an ionic crystal does not conduct electricity.
• When sodium chloride in the liquid state is considered, the ions exist separately. An ionic compound in the molten state conducts electricity because ions have the ability of movement.
Polarization-Polarizing power of a cation and polarizability of an anion
• When an ideal ionic compound is considered, the anion and cation which are its components are regarded as existing in the form of regular solid spheres. But depending on the nature of the cation and the anion which are the constituents of the ionic compound, the cation attracts the electron cloud (polarizing power of the cation) of the anion and at the same time repels the nucleus thus distorting or polarizing the anion and as a result distortion occurs in the electron cloud of the anion (polarizability and tendency to undergo polarization). If the degree of polarization is insignificant the bond remains ionic whereas if it significant electron cloud will be pulled towards the cation resulting in a considerable degree of covalent character.
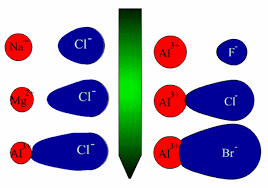 ⇓ Increase in polarization of the anion . Showing Covalent character to a considerable extent.
⇓ Increase in polarization of the anion . Showing Covalent character to a considerable extent.
Cation : If cation is Smaller in size Highly charged or both, polarizing power is high.
Anion : If anion Larger in size Highly charged or both , polarizability is high (tends to distort or polarize).
Examples : In AgF, AgCl, AgBr and AgI the ionic properties vary as follows. AgF > AgCl > AgBr > AgI
When the anion becomes larger the polarizability increases with the resulting increase of covalent character. CsI > KI > NaI > LiI
When the cation becomes smaller the polarizing power increases with the resulting increase of covalent character. MCO3 → MO + CO2 Breaking up of the group into O2- and CO2 is influenced by the polarizing power of the M2+ ion.
The polarizing power of the cations in Group II varies in the order, Be>Mg>Ca. Therefore the thermal decomposition temperatures of group two carbonates vary in the order BeCO3 < MgCO3 < CaCO3 .
Covalent bonds
• Covalent bonds are formed by keeping the bond pair of electrons common to both the atoms. Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals.
• If the electronegativity difference between two covalently bonded atoms is zero, the bond is referred as a non-polar covalent bond. Other covalent bonds are referred as polar covalent bonds.
• A bond can be formed by the overlapping of an orbital containing lone pair of electrons with the empty orbital of the valance shell of another atom. The bond formed in this way is called the dative bond. There, the species which give the lone pair of electrons is called the donor group (Lewis base) and the species that receives the electrons to form the bond is called the acceptor group (Lewis acid).
Metallic bonds
The electrons in the valence shell of metallic atoms are loosely bonded to the atom. Therefore, there is a tendency for the metallic atoms to release the electrons in valence shell and exist as positive ions. As a result a system is formed in which positive ions are immersed in a sea of electrons which were released from the metal atoms. The positive ions and the sea of electrons get attracted electrostatically to form metallic bonds.
Metals conduct electricity due to the presence of free electrons.
Strong metallic bonds are formed when the size of the metal ion decreases, when the charge of the metal ion increases and when the number of electrons contributing to the metallic bond increases.
When the strength of metallic bond increases melting point of the metal also increases.
Attractions that exist in covalently bonded molecules or in ionic compounds or in metalic latices are referred as primary interactions.
