A structure where the covalent bonds in a covalent molecule or an ion group are represented by Lewis dot symbols, with shared pairs of electrons shown by a short line or a pair of dots (or a pair of dot – cross), and the lone pair of electrons on each atom by pairs of dots or pairs of crosses, is called a Lewis structure. In the Lewis structure only the valence electrons are shown.
Example – Consider H2O molecule.
Lewis dot – cross structure of the molecule of water
Lewis structure of the molecule of water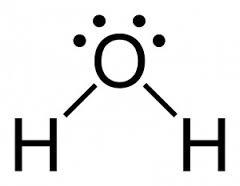
From a Lewis structure information can be obtained about the way that atoms are attached in a molecule, how the number of electrons in the valence shells are distributed and also about the type of the bonds formed. But the Lewis structure does not give information about the shape. By obtaining the number of bond electron pairs and the number of lone pairs situated around the central atom of a molecule from the Lewis structure, the shape of the molecule can be predicted by applying the valence shell electron pair repulsion(VSEPR) theory .
There are occasions where two or more Lewis structures exist for a given same molecule or the ion group which differ from one another only due to differences in the electron arrangement. Such structures that exist for a certain molecule are known as resonance structures. The actual structure of the molecule is not the same as any of these but is a more stable different structure formed by the hybridization of resonance structures. The resonance structures/resonance forms/canonical structures do not have independent existence, but merely drawn for convenience.
