• The functional group of the carboxylic acids is the carboxyl group. In the carboxyl group there is a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group attached to that carbon atom.
• Carboxyl group is a polar functional group. Due to the polarity of C – O and O – H groups it forms intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Relative to the aldehydes and ketones with equal relative molecular masses, the boiling points of carboxylic acids are higher.
• Carboxylic acids of C1 to C4 dissolve well in water. When the number of carbon atoms increases solubility decreases. Aromatic carboxylic acids are water insoluble and exist as solid crystalline substances. Almost all the carboxylic acids are soluble in organic solvents.
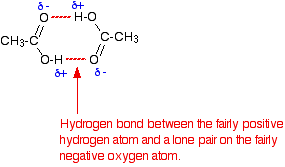
• The ability to form dimeric structures where carboxylic acid molecules are attached by hydrogen bonds as pairs is also a reason for the high boiling points of carboxylic acids.
Existence of carboxylic acids as dimer structures attached by hydrogen bonds is shown below.
Reactions involving the cleavage of O – H bond
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The above compounds react with Na2CO3 in the same way that they react with NaHCO3.
The acidic strengths of alcohols, phenols and carboxylic acids vary as follows.
Alcohols < Phenols< Carboxylic acids
The carboxylic acids attain the following equilibrium in an aqueous solution
The equilibrium point of the above equilibrium is situated more shifted towards the right side relative to the corresponding equilibrium attained by the phenols. The reason for this is that the stability of the carboxylate ion relative to the carboxylic acid is greater than the stability of the phenoxide ion relative to phenol. The carboxylate ion is a resonance hybrid of the following structures.
The stability of the carboxylate ion is due to the delocalization of the negative charge between two equivalant electronegative oxygen atoms.
• With PCl3/ PCl5
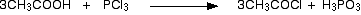
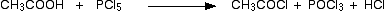
• With alcohols
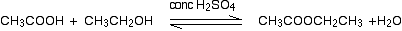
• Reduction of carboxylic acids with LiAlH4
Carboxylic acids give alcohols when reduced with LiAlH4 which is a very strong reducing agent. Carboxylic acids and their derivatives are not reduced by NaBH4.
