• Amines can be defined as compounds where alkyl or aryl groups are attached to nitrogen in place of hydrogen atoms in ammonia.
Amines are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary. Unlike the alkyl halides and alcohols, the amines are classified according to the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
The compounds in which an alkyl or an aryl group is attached in place of one of the three atoms of hydrogen in ammonia are called primary amines.
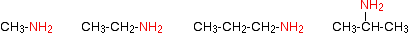
The compounds in which two alkyl or aryl groups are attached in place of two atoms of hydrogen in ammonia are called secondary amines.
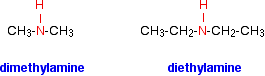
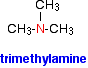
The compounds in which three alkyl or aryl groups are attached in place of the three atoms of hydrogen are called tertiary amines
• The compounds in which at least one aryl group is attached to the nitrogen atom are called aryl amines.
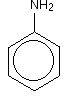
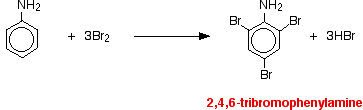
• Aniline readily reacts with bromine water to give a white precipitate as -NH2 group activates benzene ring.
• Amines act as nucleophiles due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The following are some of the reactions of primary amines with various reagents where the amine acts as a nucleophile.
(i) With acid chlorides

(ii) With aldehydes and ketones
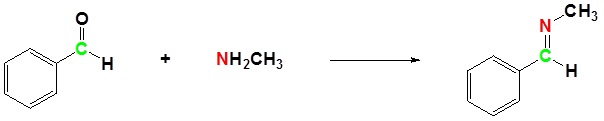
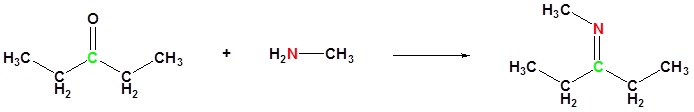
(iii) With alkyl halides

(iv) With NaNO2/HCl (Nitrous acid)
Primary amines react with nitrous acid to form diazonium salts. As alkyl diazonium salts are unstable they rapidly convert to alcohols with the evolution of nitrogen gas.
![]()
Aromatic diazonium salts formed from aryl amines are more stable particularly at low temperatures.
