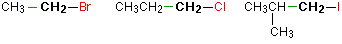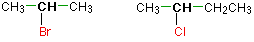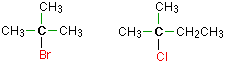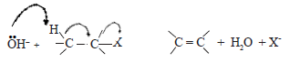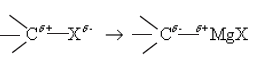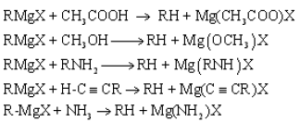Haloalkanes are colorless, sweet-smelling liquids. The lower members like methyl chloride, methyl bromide and ethyl chloride are colorless gases while members having very high molecular masses are solids.
Solubility
Haloalkanes are not able to form hydrogen bonds with water and, even though they are polar in nature, they are practically insoluble in water. However, they are soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, ether, benzene, etc.
Density
Chloroalkanes are lighter than water while bromides and alkyl iodides are heavier. With the increase in the size of the alkyl group, the densities go on decreasing in the order of :
fluoride > chloride > bromide > iodide.
Boiling points
The boiling points of alkyl chlorides, bromides and iodides follow the order RI > RBr > RCl where R is an alkyl group. With the increase in the size of halogen, the magnitude of Van der Waals forces increases and, consequently, the boiling points increase. Also, for the same halogen atom, the boiling points of haloalkanes increase with increase in the size of alkyl groups.