HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Absorption of nutrients
Absorption of nutrients
1) Diffusion
2) Facilitated diffusion – ATP is not required
3) Active transport – ATP is used
Balance diet
Dietary fibers
1) Provides bulk to the diet and helps to satisfy the appetite
2) Stimulates peristalsis
3) Attracts water, increasing bulk and softness of faecus
4) Increases frequency of defecation, preventing constipation
Example: – Colo-rectal cancer
Disorders in the alimentary canal
2) Prolonged starvation
3) Consumption of alcohol
4) Suffering from some diseases such as tuberculosis, syphilis etc.
5) Prolonged use of aspirin
Control

 is opened to the outside and they relay by mouth which is bounded by the lips and is continuous with the pharynx posteriorly
is opened to the outside and they relay by mouth which is bounded by the lips and is continuous with the pharynx posteriorly
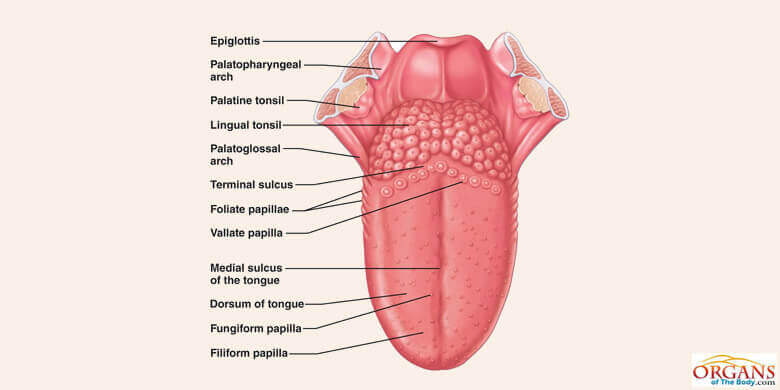 is attached to the bone by its base under the floor of the mouth by the frenulum made up of skeletal muscles and lined by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
is attached to the bone by its base under the floor of the mouth by the frenulum made up of skeletal muscles and lined by non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium

Functions of the tongue

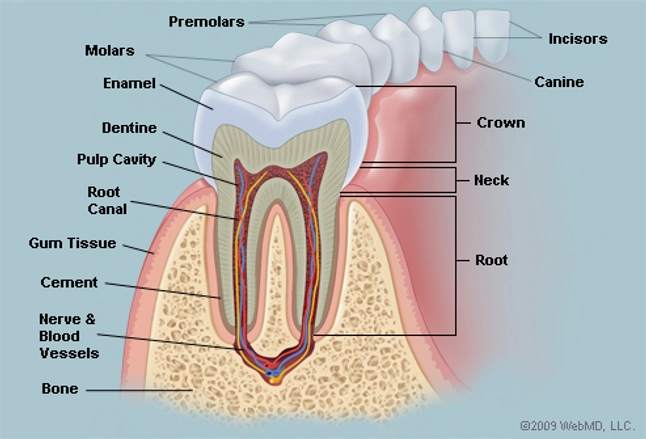

 are embedded in the sockets of the jaws.
are embedded in the sockets of the jaws.
 of permanent tissue and deciduous tissue differs
of permanent tissue and deciduous tissue differs
DENTAL DISEASES
Factors contributing to the dental disease

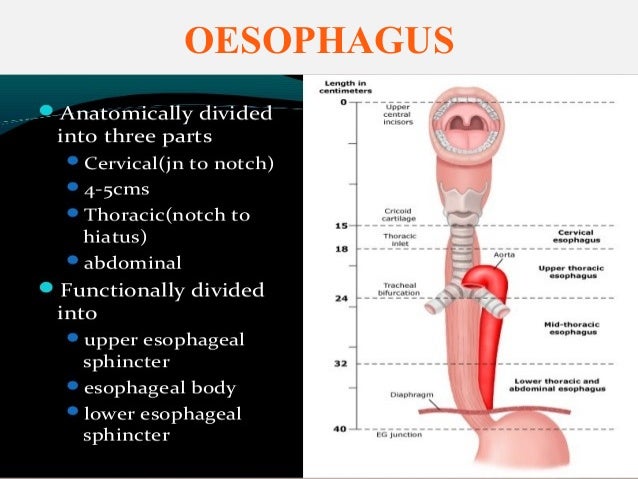 lined by stratified squamous epithelium
lined by stratified squamous epithelium
 is lined with secretory cells, Goblet cells, Parietal cells and chief cells
is lined with secretory cells, Goblet cells, Parietal cells and chief cellsHistological structure of the small intestine 
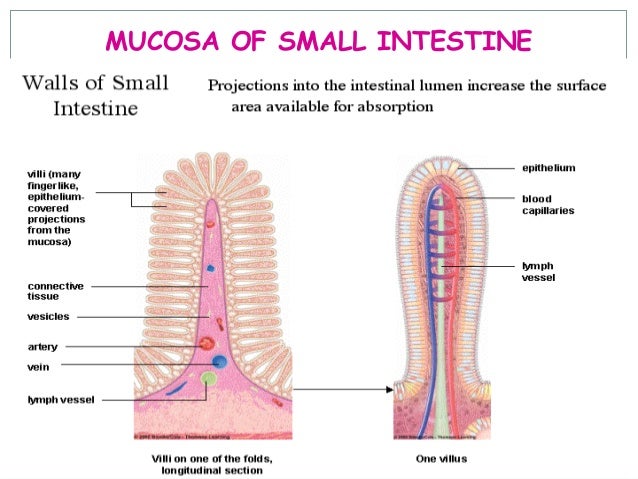

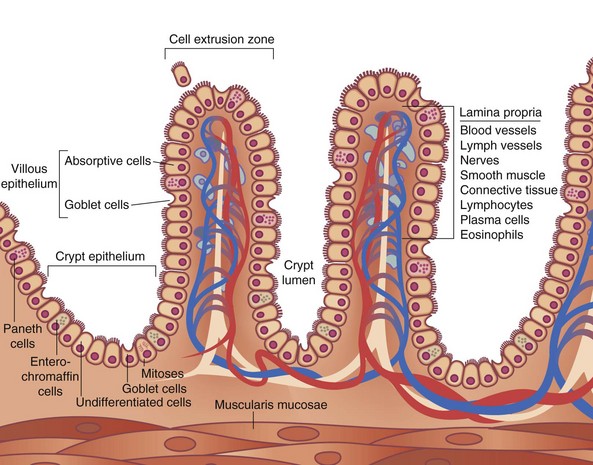
Duodenum
Intestinal juice
Adaptations of a small intestine for efficient digestion and absorption
Functions of small intestine


Histological structure of large intestine.
Numerous lymph nodes are present in lamina propria and in submucosa.
Functions of large intestine
Eg:- Escherichia coli
Enterobacter aerogenes.
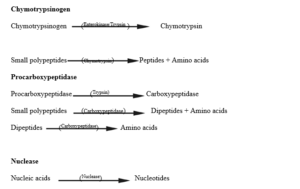
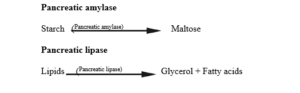
Pancreatic juice
Bicarbonates
functions of enzymes in the pancreatic juice includes 




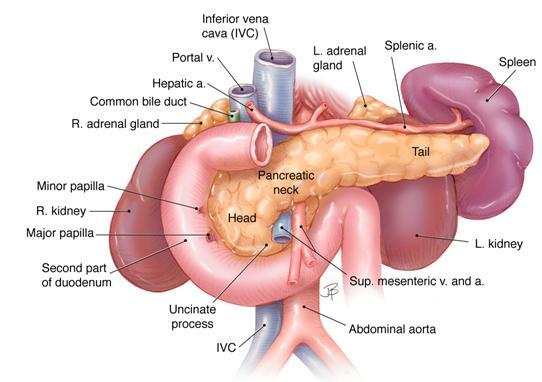
Location
Or
Structure
Histological structure of liver


Functions of liver
1) Synthesis or production
Eg :- albumin, globulin, fibrinogen
2) Storage Fat soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
3) Protection
Example :- alcohol, Nicotin, microbial toxins.
4) Formation of excretory substances.
5) Production of heat.
6) Elimination or destroying
7) Regulation
1) The body is unable to store absorbed amino acids and those not required for protein synthesis are deaminated in the liver. The keto acids can be used for respiration.
2) Transamination – Removes the Amine groups of amino acids and attaches to form the new non-essential amino acids.
Bile
Sodium glycoholate
Functions of the bile
