Autotrophic nutrition – is of two types:
Heterotrophic nutrition – organisms feed on an organic source of carbon. All animals and fungi and majority of bacteria are heterotrophic
Modes of heterotrophic nutrition
Development of the Digestive System in animals to facilitate Holozoic nutrition
Mutualism
Parasitism
Commensalism It is a close association between two living organisms of different species which is beneficial to one and does not affect the other. e.g., Sea anemone and hermit crab, epiphytes (orchids)

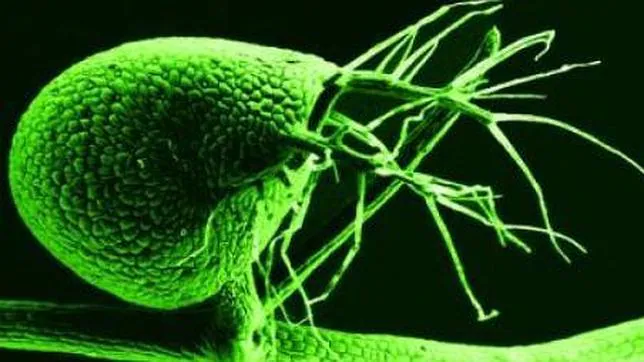
 , Drosera
, Drosera 
 , Utricularia
, Utricularia