Hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies incompressible fluids at rest.
Density
The density of a substance is its mass per unit volume. 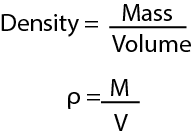
Relative density
the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a standard, usually water for a liquid.
Pressure in a static fluid When a fluid is at rest , a force only acts at right angles.This is because a fluid cannot sustain a tangental force .When a fluid at rest forces simply act normal to the surface .

where 


Pressure is a scalar quantity ,it has no fixed directions.The direction of the force exerted by the liquid is decided by the orientation of area present to the liquid.
Expression for fluid pressure
 If we consider atmospheric pressure , say it’s Po , then the pressure at depth h is given by P = Po + hρg
If we consider atmospheric pressure , say it’s Po , then the pressure at depth h is given by P = Po + hρgIn a static liquid, pressures at same level in a same liquid are equal. 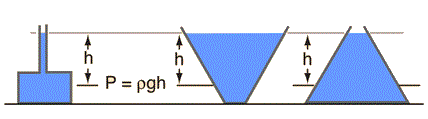
Pressure of atmosphere
Our Earth is surrounded by air upto a considerable height.This envelope of air surrounding the Earth is called atmosphere.Since air has weight, a column of air is capable of exerting pressure.It is first measured by Toricelli.
Atmospheric pressure Po = hρg
1 atm=1.014 bar= 760 mmHg 1 torr = 1mmHg
Manometer Manometer consist of U tube, it is used to find the difference in pressures between the gas enclosed in a vessel and atmospheric pressure.
Pressure at x = Pressure at y
Unknown Pressure P = Po + hρg
Determination of density of coconut oil using U tube
First take the water in the U tube then add coconut oil to one of the arm and give some time to settle.After it settles measure the height of coconut oil(h2) and water(h1) from common interface. To take several measurements add coconut oil and measure the heights from the common interface.
Hare’s apparatus
Arrange the above setup as shown in the figure .Suck the air from the tube,then the liquids in both arm rises upto maximum level.Then measure the heights hw and hl.Then reduce heights and take several sets of reading.
Pascal’s law states that a pressure change occurring anywhere in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
Incompressible fluid means due to the pressure the density of the fluid
The pressure acting on both pistons in a hydraulic jack is equal.
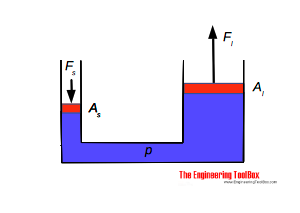
The force equation for the small cylinder Fs = p As
where Fs = force acting on the piston in the small cylinder (N) , As = area of small cylinder (m2) , p = pressure in small and large cylinder (Pa, N/m2)
The force equation for the large cylinder Fl = p Al
where Fl = force acting on the piston in the large cylinder (N) , Al = area of large cylinder (m2) , p = pressure in small and large cylinder (Pa, N/m2)
Fs / As = Fl / Al
or
Fs = Fl As / Al
It states that when a body is fully or partially emerged in an incompressible fluid at rest, it experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
When an object is placed on the surface of a liquid it will either float or sink. This depends upon two forces:
You know that the weight of an object is the product of its volume and its density. Hence,
W1 = Volume of the object (V) x Density of the object (d1)
W2 = Volume of the liquid displaced (V) x Density of the liquid (d2)
Let us see what are the different situations under which a body floats, sinks or remains submerged completely at any level in the liquid.
Case 1:
When the weight of the object W1 is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced W2, the object will stay in the position of rest completely immersed in the liquid. Here,
W1 = W2 or
V x d1 = V x d2 or d1 = d2, then the object will be floating completely immersed in a liquid as shown in figure below.

Weight of the object is equal to the weight of the liquid
Case 2:
When the weight of the object is greater than the weight of the displaced liquid, the object will sink. Here,



Thus, when the density of the object is greater than the density of the liquid, the object will sink.

Weight of the object is greater than the weight of the liquid displaced.
Case 3:-
When the weight of the object is less than the buoyant force (upthrust), the object will float on the surface of the liquid.
When the object floats, only a part of it is submerged in the liquid and volume of the liquid displaced will be less than its own volume. Let V’ be the volume of the liquid displaced by the submerged part of the object. Here




Density of the solid is less than the density of the liquid and hence the object will float.

Weight of the object is less than the weight of the liquid displaced
Hydrometer is an instrument used for determining the density of a liquid. It usually consists of a glass float with a long thin stem which is graduated. The glass float is a large hollow bulb which increases the buoyancy so that the hydrometer floats. The narrow stem increases the sensitivity of the hydrometer. The bottom of the hydrometer is made heavier by loading it with lead shots so that it floats vertically.

