Work
The word work is used only in those cases where there is a force and a displacement occurs in the direction of force.
Work done = Force acting on the body × Distance moved in the direction of force
W = F × S
[W] = ML2T-2
Unit – kgm2s-2 = joule
1 J – 1 joule is the work done by a force of 1N acting through a distance of 1m in the direction of force.
Power
Power is the rate of doing work.
[P]=ML2T-3
Unit – kgm2 t-3 =Js-1 Watts
1Watt – Capable of doing work at the rate of 1Js-1 is said to possess a power of 1W
Work done by applied force W=F×S
Work done by applied force in unit time = F×S/t
Power=F×V
Ability to do work is called energy.
An object has kinectic energy due to its motion.
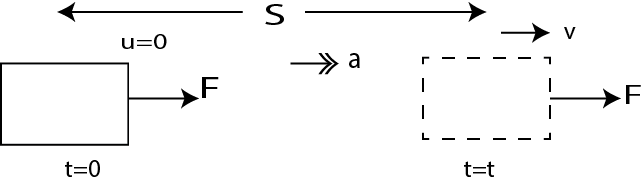
Kinetic Energy = ½mv²
Gravitational potential energy is a energy due to the position of the object.
Gravitational potential energy= mgh
Elastic potential energy is Potential energy stored as a result of deformation of an elastic object, such as the stretching of a spring. It is equal to the work done to stretch the spring, which depends upon the spring constant k as well as the distance stretched. According to Hooke’s law, the forcerequired to stretch the spring will be directly proportional to the amount of stretch.
F = -kx |
x- extension k-spring constant
Elastic potential energy=½kx² =work done =area of the triangle
Mechanical energy is the sum of the potential and kinetic energies in a system. The principle of the conservation of mechanical energy states that the total mechanical energy in a system (i.e., the sum of the potential plus kinetic energies) remains constant as long as the only forces acting are conservative forces.
