- Total number of people who between minimum a maximum age limits and who are willing to after their labour during a particular period of time to produce goods and services which have economics value expecting a salary/wage or an economic gain are known as labour force.
- Persons who are not included in Labour force
- Housewives
- Full time students
- Totally disabled
- Voluntarily idle
- When calculating labour force in Sri Lanka only minimum age limit that is 10 years is considered but maximum age limit is not taken to account.
- All employed and unemployed people who are expecting a salary or an economic benefit( it one week before counting) are included in the lobour force in Sri Lanka.
- All the individuals who are above 10 years of the total population of Sri Lanka and who are able to work are considered to be in working age population.
Partivipation Rate
- Indicating labour force as a percentage of people who are able to work is labour force partivipation rate.
The factors which determine the labour force are as follows:
- Population size
- International migration
- Age structure
- Male and female population
- Civil status
- Level of education
- Social protection services
- Urbanization
- Health and neutrinos level
- Social, cultural and religions concepts
- Population growth takes place due to natural increase and net migration ratio.
- Population is calculated using population growth rate.
- Population growth rate measures how the population has increased in the present year compared to the previous year increase in present year population comparing to the last year population.
Natural Growth
- The difference between crude birth and crude death in a particular year is called natural growth.
- Speed of the natural growth is measured by the natural growth rate.
Crude Birth
- The measure that measures the number of births in a country is known as crude birth rate.
Changes in the population of Sri Lanka during last years
- Significant decrease in population growth rate
- Net migration is an important factor that effects population growth in recent years
- Population increased by 5.2 millions from 1981 to 2007
- Differences can be seen in age structure
- Decrease in the percentage of child population
- Decrease in the working age of population
- Increase in aged population
- Decrease in infant mortality ratio
- Decrease in natural growth rate
The demand is for various quantities of goods which are ready to be purchased at various prices when other factors affecting demand remain constant.
Demand can be categorized as follows.
- Individual demand
- Market demand
The individual demand is for various quantities of goods, buyers are ready to buy at various prices at a certain time period.
The market demand is a sum of various quantities of goods which are ready to be bought at various prices by all buyers in a market for a certain good, at a certain time period.
The theory of demand is analyze the changes of demand according to changes of the determinants of demand.
The factors mentioned below affect determine the market demand.
- The key determinants of demand can be listed as below.
- Price of the good concerned (P)
- Prices of related goods (Substitutes and complementary goods) (Pn)
- Consumer income (Y)
- Consumer taste (T)
- Future expectations (Ex)
- Number of buyers and its composition. (N)
That, it is possible to show the relationship between the individual demand for any good and its determinants, as an equation given below.
Qdx = F (P, Pn,Y,T,Ex)
The relationship shown by this is named “individual demand function”.
That, it is possible to show the relationship between the market demand for any good and its determinants, as an equation given below.
Qdx = F (P, Pn, Y, T, Ex, N)
That, the relationship shown by this is named “Market demand function”.
- If sufficient income is not earned to buy food and other needs to get the calories
intake, is explained as absolute poverty.
- Relative poverty is caused by inequal distribution of income.
Two sides of Poverty
- Income poverty
- Consumption poverty
Basic Poverty
- If one cannot earn income which is sufficient to provide basic needs and minimum consumption level it is called basic poverty.
Human Poverty
- According to the definition of the U.N.O. the situation that deprived people of
choosing opportunities to live a happy, healthy life with freedom, self esteem,
recognition in the society is termed as human poverty.
National Poverty line
- The minimum expenditure needed to get food and non-food items in order to survive and to maintain a good behaviour is called national poverty line.
Types of Human poverty indices
- Human poverty index 1 (HPI -1)
- Human poverty index 2 (HPI – 2)
- There is a class difference between low income class and high income class in any society which has market system.
- It is called inequality of income distribution.
Types of inequality of Income distribution
- Relative distribution of income
- Absolute distribution of income
Lorenz Curve
- Nature of the relative income distribution can be illustrated by Lorenz curve.
- The inequality of income distribution will be reduce a when the lorenz curve gets closer to the equal distribution curve.
- The inequality of income distribution will be increase when the lorenz curve is faraway from equal distribution curve.
Gini Coefficient
- The amount of inequal distribution of income shown as lorenz curve can be measured by the Gini coefficient.
- The inequality of income distribution increases when the Gini coefficient is closer to 1
- The inequality of income distribution decreases when the Gini coefficient is closer to 0 (zero)
- Gini coefficient is equal to 0 (zero) when there is no inequality of income
Any dynamic phenomenon could be identified as a variable
- Economics studies the relationship of the economic variables
- Various relationships exists among the variables
- Any variable initiated to change the other variable is known as independent variable.
- Changes that have taken place due to the changes of the independent variable is called
the dependent variable
- In accordance with the behavior of the independent variable ,the quantity of production
and consumption could be shown by using a schedule.
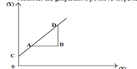
If X is considered as the independent variable and Y as the dependent variable , changes of Y on X could be shown on a straight line in a graph as follows
![Untitled-1gr]()
- By drawing the impact of the above variables in a diagram, AB straight line could be
derived
- Relationship between the independent and dependent variables related to the straight line
could be written as an equation such as:
Y= mx+ c
Y = mx + c in the equation, Y = dependent variable, X = independent variable
M = gradient/ slope, C = intercept
When there is a positive relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable, the graph has a positive slope and this can be shown as follows.
![Untitled-1fgtr]()
When there is a negative relationship between independent variable and the dependent
variable, the graph shows a negative slope as follows.
![Untitled-2nhh]()
The ratio of the differences in independent variable and the dependent variable is the slope or gradient of the line and it could be computed as follows
Gradient/slope(b) = Difference in the horizontal axis / Difference in the vertical axis
The equation of a straight line : Y =a+ bx is applied in economics in this equation:
Y = dependent variable
a = Intercept
b =Gradient/ slope
x = Independent Variable
Slope of a straight line is constant
- When the independent variable is Zero (0) the value given to the dependent variable is called the intercept (a)
- If the independent and dependent variable of a straight-line, are given the above equation could be developed,
- When the simple equation has been given the graph can be developed from it.
- The development achieved through economic development, social development, conservation of the environment is known as sustainable development.
- Countries enter into the sustainable development approach due to the following reasons:
- Conservation of environment
- To protect natural resources
- Utilization of environmental resources and natural disasters affect the sustainable development, examples of them are:
- Unlimited consumption of natural resources
- Increase in global warming
- Melting of ice mountains
- Climatic changes
- Depletion of the ozone layer
- Deforestation
- Water pollution
Capital required for Sustainable development
- Physical capital
- Human capital
- Natural capital
- Social capital
Aim of the Sustainable development concept
- Maintain a balance between the Economic development
- Increase in natural resources and Environment
Pillars of Sustainable development
- Economic development
- Social development
- Protection of environment
The market which exchanges consumer goods is defined as the goods and services market
The market which exchanges land, labour and capital is defined as the factor market
- Households demand goods and services and firms demand factors of production
- Firms supply goods and services for consumption and households supply factors of
production
- Demand for factors of production exists, is due to the demand for goods and services
- There is a derived demand for factors of production while there is a direct demand for
consumer goods
- Demand for goods and services for consumption depends on their marginal utility and
the demand for factors of production depends on the marginal productivity of these
factors.
- Factor earning will be determined by factor prices and the amount of factors exchanged
factor market.
- Factor earnings consist of transfer earnings and economic rent.
- The minimum income expected by a particular factor remaining in current use is identified
as transfer payments.
- Any earnings above transfer payments is the economic rent.
- Demand for factors of production exists, due to the demand for goods and services
- Economic development is a changing process of the economy and increases the economic development of the life of the people and increases the quality of life.
- There is development in the social, political environmental and cultural sectors with the economic development.
- Economic development is a multi-dimensional process as it develops several sectors in the economy.
- The following conditions should be fulfilled to achieve Economic development together with Economic growth:
- Structural changes in the production process in the economy
- Increase in productivity of production resources / Factors of production
- Improvement in production techniques and in technology
- Modernization
Individual indices to measure the progress of Economic development
- Per capita G.D.P
- Relative income distribution
- Life expectancy
- Literacy rate
- Gini Coefficient
- Labour force participation rate
Composite Indices
- Physical quality of life index
- Human Development index
- Human poverty index
- Continuous increase in real gross national production is called economic growth.
- It shows long term expansion of production potential.
- It illustrates quantitative changes in the production of goods and services in the economy.
- Economic growth is measurable.
Advantages of Economic growth
- Eleminates poverty when achiveing high levels of living standards
- Increase in income
- Businesses or Entrepreneures can earn higher profits
- Increase in rate of employment
- Increase in creditability in business
- Decrease in budget deficit
Costs of economic growth
- Risk of inflation
- Negative effects of increase in production and consumption on the environment
- Inequalities in distribution of income and wealth
- Regional disparities
- Harmful to sustainable development
- Enviornmental degradation
- Increase in global warming
- Loss of international co-operation for the development of human welfare since the country is catogerised as a high income country