 Products can be presented as shown in the following flow chart:
Products can be presented as shown in the following flow chart:
| Needs | Wants |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aims of Business
Communication can be analyzed as sending information from one party to another party or many parties, receiving information, understanding information and distributing them
Communication is important for business activities in the following ways.
Examples
• To exchange ideas between relevant parties in business transactions
• To maintain employer-employee relationship
• To promote marketing activities
• To manage human and physical resources well
The communication process can be shown in a diagram as follows
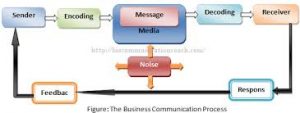
The following are the elements of a communication process
• Sender
• Message
• Mode
• Receiver
• Response
• Feedback
Characteristics of effective communication can be listed as follows
• Accuracy
• Conciseness
• Completeness
• Clarity
• Courtesy
• Concreteness
• Consideration
• Cost effectiveness
• Speed
The following facts should be taken into consideration when preparing a message
• Nature of the message
• Ability for receiver to understand
• Completeness
• Conciseness
• Accuracy
• Concreteness
• Courtesy
The following methods are used for communication
• Verbal method
• Written method
• Signals and symbols
The following are examples of the ways communication takes place through different methods of communication
The external and internal communication methods that a business institution uses can be listed as follows.
Internal
• Notice board
• Meetings
• Intercom
• Circulars
• Letters
• Memos
• Reports
External
• Telephones
• External letters
• External notices
• Posters
• Banners
• Gazettes
• News papers
• Television
• Fax
Some of the modern electronic communication methods can be explained as follows
Internet A computer network which covers a wide range or a computer network established interna- tionally. Here the information inserted from different places can be obtained using personal computers
Electronic mail The exchange of messages from a computer to a computer through the internet is called electronic mail. Notes and long documents too can be sent through electronic mail by typing the e-mail number of the receiver of the message using a modem or a terminal connected to a personal computer.
Intranet A creation of wide relationships inside a firm through Internet based on web technology and internet standards. Based on the internet this institutional network facilitates one to approach the data which are in the business institute.
Voice mail According to this work system, the message given by the sender verbally over the phone is reflected through networks and stores in a disk or records it in order to obtain same later.
Fax machines This is a type of electronic equipment which can quickly send documents including letters and pictures through an ordinary telephone system. In the fax system, the fax machine which sends the message reflects photo copies of relevant documents through digital technology to the fax machine which receives it.
Intercom A personal telephone network prepared in the institution by using a telephone network in order to exchange information within the institution
There are barriers such as the following to effective communication
• Lack of knowledge of the use of new technological methods
• External barriers involved in the use of communicating tools
• Using out dated communicating methods
• Barriers along the path of communication flow
• Weakness of communication plans
• Language problems, knowledge, attitudes etc
. • Steps should be taken to overcome the barriers to communication
• There are advantages and limitations in communication
Written communication –
Advantages
• Ability to present information with greater details
• Ability to prove that information was communicated and received
• Ability to communicate data, notes, tables etc., easily
Limitations
• Problems in understanding information
• Difficulty in communicating information when reading ability is weak
• Information getting distorted when communicating
Verbal communication
Advantages
• Ability to present a problem with more details after discussing it.
• Meeting both the sender and the receiver
• Ability to present information more quickly and confidentially.
Limitations
• Arising out of language problems
• Problems of exchanging information with parties who are verbally weak
• Inability to prove that information was communicated
Communication with signals and symbols
Advantages.
• Ability to present information briefly and clearly.
• Higher level of accuracy of information.
• Ability to understand information easily.
Limitations.
• Problems in exchanging information with parties who have problems and weaknesses in eye
sight.
• Barriers involved in communicating information through distortion of signals and symbols.
• Difficulty in understanding certain signals and symbols.
Transport plays an important role as an auxiliary (support) service in fulfilling needs and want of business enterprises and individuals.
role as an auxiliary (support) service in fulfilling needs and want of business enterprises and individuals.
• Transportation is not just a mode only. It is also a system made up of some elements with a balanced development.
These elements of the transport system can be explained as follows
• Way :- Different means used for transportation.
Eg: Highways, railways, waterways, airways, pipelines
• Mode :- Vehicles running on various ways Eg: Motor vehicles, carts, bicycles, passenger trains, good trains, boats, ships, helicopters, air planes.
• Power :- The energy used to drive the vehicles used in each mode. Eg: Natural power such as man power, animal power, wind, sunlight and coal, mineral oil, electricity, gas.
• Terminal :- The places where the modes of transport use to stop the vehicles. Eg: Bus stand, railway station, airport, harbour
Some advantages of the highway transport method are mentioned below:
• Ability to select a mode according to the needs
• Island wide availability
• Ability to use highways whenever necessary.
• Mostly the same mode of transport can be used until the end of the journey.
• A speedy method for short distance journeys.
Some limitations of the highway transport method are mentioned below.
• Difficulty in transporting large stocks at the same time.
• Difficulty in maintaining highways.
• Delays and a greater number of accidents
• Interruptions due to bad weather conditions.
Some advantages of railway transport method are mentioned below.
• Ability to transport a large stock and a large number of passengers at the same time.
• Greater security than highway transport.
• Ability to use compartments according to the nature of the goods.
• Charges are moderate compared to other transport methods.
• Ability to get various facilities such as canteens, sleeping births, observation rooms etc.
The following are some of the limitations of railway transport.
• Non-availability of island wide railway lines.
• Inability to get the service whenever the necessity arises.
• Due to the inability of using the same method up to the end of the journey, other transport methods have to be used.
• Delays due to non performance of signal lights, weak conditions of railway lines etc.
Some advantages and limitations of waterway transport are mentioned below. Advantages:
• Facilitates international trade.
• Ability to transport large quantities.
• Ability to select vessels according to the nature of goods.
Limitations:
• Limited availability
• More time consuming
Some advantages and limitations of airway transport method are mentioned below. Advantages:
• High speed.
• Suitable for perishable goods.
• No costs for maintaining airways
Limitations:
• Not suitable to transport huge and very heavy goods.
• High transport cost.
• Greater tendency for accidents.
• Non availability of service when needed.
• Discuss the importance of transportation to businessmen as well as to consumers.
of transportation to businessmen as well as to consumers.
It is possible to list the facts that should be taken into consideration, when selecting a suitable transport method as follows
• Nature of the goods
• Distance
• Speed
• Safety
• Cost
• Capacity
• Availability
• Standards and international norms
The following are the documents used in relation to transports methods
Transport method Documents used
Highway transport
• Transport of goods : Goods delivery note
• Transport of passengers : Ticket, season ticket Pass for free travel
Waterway transport
• Transport of goods : Bill of lading
• Transport of passengers : Ship entry ticket
Airway transport
• Transport of goods : Airway bill • Transport of passengers: Air ticket
Railway transport
• Transport of goods : Consignment note
• Transport of passengers : Ticket/ Season ticket/ railway warrant
New trends are also developing in the transport field and the following are some examples for them.
• Transport through tunnels (subways)
• Construction of flyovers
• Construction of highways
• Use of cable cars
• Use of electric trains
Features included in insurance are the person who desires to obtain cover by paying the
premium periodically and the organization which agrees to compensate the insured for
any losses or damages, specified in the agreement.
• Insurance is based on the pooling of funds where policy holders pay a premium into a
pool. The pool of money so created is then used to be pay compensation to those who
make claims.
• In insurance, risk is defined as a monetarily estimated damage.
• The risks may be divided into insurable risks and non- insurable risks.
• Features of insurable risks are given bellow
• Predictability
• Causality
• Unconnectedness
• Verifiability
Reasons for the risks could be examined on the basis of place, time and value.
Examples of non- insurable risks are given below.
• Business risks emerge due to natural reasons as expiry periods, depreciation etc.
• Risks are decided on an individual’s incapabilities, where he or she fails her examination, or loses someone’s love.
• Business risks occur due to incorrect decisions taken by the management.
Necessity of insurance can be explained as followings.
• The investors are encouraged to insure against business risks.
• A financial compensation could be obtained to safeguard those who lose their lives under tragic circumstances or are disabled due to illness.
• A Substantial proportion of the nations savings is channelled through insurance companies to the capital market, where it is invested in a wide range of enterprises.
• Marine insurance helps the progress of international trade.
• The contract between insurer and the insuree is called an insurance agreement. It is a written agreement between the insurer and the insuree which is arrived at after the insurer’s acceptance of the application.
Parties involved in insurance agreements are, listed bellow
• 1st party(Insurree) : A person who is covered against possible losses incurred; he is entitled to receive compensation.
• 2 nd party (Insurer): The institution or the organization that undertakes to compensate for risks.
• 3rd party : All parties other than those who are involved in the insurance agreement
The essential requirements for an insurance agreement, are given bellow
• There should be an intension of forming a legal relationship.
• Suggestion
• Legalization or legality
• Acceptance
• Capabilities of creating a legal agreement between the two parties.
An insurance policy is a document, which is issued by an insurance company to the insuree, for the insurance agreement obtained on life or on any property.
Must follow certain insurance principles to run the insurance business.
The following are the principles of insurance.
• Insurable interest
• Utmost good faith
• Indemnity
• Contribution
• Subrogation
• Proximate cause
Insurance companies permit you to insure against a risk only if you have an insurable interest in that event , that is to say if the event does occur, you must suffer some kind of loss or some kind of liability.
Example : According to insurable interest a wife can insure her husband and a husband can insure his wife when applying for life assurance. An owner of property has the insurable interest to insure his own property.
The person who insures must disclose all the details of the objects (Property, Life etc.) to the insurer and this is known as utmost good faith.
The principle of indemnity means, to restore the insured to the position to compensate for the loss.
If a property is insured with a number of insurance companies, all companies will jointly pay compensation, each contributing a share in proportion to the value for which it was insured. This is known as the principle of contribution.
Subrogation is a sub principle of indemnity and this implies that when an insuree who accepts the compensation payment made for exact damage by the insurance company, he or she does not have any further right over the things insured. Any money raised through the sale of the asset belongs to the insurance company, not the policy holder.
Sub principle of proximate cause implies that the root cause of the event known as proximate cause, and this must be covered by the policy for a claim to be valid. That is unmentioned risks cannot be covered by the insurance agreement.
Insurable interest utmost good faith, and proximate cause are the basic insurance principles that only apply to life assurance.
Principle of indemnity, subrogation and contribution are the basic principles which are not applicable to life assurance.
The objective of life assurance is providing assurance against unexpected losses, such as death, disability and is a very important means of saving for old age.
• The benefit of life insurance is providing financial benefits to the dependents of the policy holder or providing compensation to the insuree in the event of death or bad injury caused by any events.
• Life assurance is to compensate only during a specified period. Insurance premium, interest and bonuses could be gained by the insuree if he lives and in the event of death of a policy holder, the insured value could be got by the dependents or the person who is mentioned in the agreement.
• Fire insurance policies provide cover against any damage to insuree’s property or losses arising from fire
Under fire insurance policy can cover certain against certain additional risks on payment of an additional premium. They are:
• Riots/ Rivalries / strikes
• Explosions
• Electro damage.
• Earthquakes
• Floods, droughts, cyclones
• Plane crash ( aviation)
• Losses incurred by disorder or quarrels
• Theft and burglary insurance policy (Can be obtained to) provide cover against the loss of goods through burglary, housebreaking
• Natural accidents policy provides cover against the losses from Tsunami, drought, cyclone etc.
• Marine insurance policy covers the loss of both ships (hull) and the cargo or merchandise carried by the vessel.
• Marine insurance is categorized into two sections. They are hull insurance and cargo insurance.
• The marine insurance policy is provided, as policy for all risks, policy for complete damage, port risk policy.
• Hull insurance policy could be subdivided into time policy, valued policy open cover policy. • Motor vehicle insurance policy covers owners, passengers, injuries to third parties on public roads plus damage to the insuree’s vehicle.
Under motor vehicle insurance policies available following
• Full insurance (Comprehensive policy)
• Third party, fire and theft insurance
• Minimum third party insurance
• Full insurance covers damage to the insuree’s vehicle passengers, injuries to third parries and damage to property of the third party
• Third party fire and theft covers damage to other people’s property from theft of vehicle and for fire damage, caused by riots or a rivalries.
• Minimum third party covers only injuries to third parties and property and it is a minimum legal requirement. This is compulsory under the law of the country.
• All employers are required by law to insure their liability to compensate their employees against disease or injury arising from their employment.
• Goods on transit insurance covers the goods in transit from the time of loading and until they are unloaded and while transporting on land and by sea.
• Transit cash insurance policy covers the loss of money while being taken from one place to another.
• Product liability covers damage which may occur in consuming products by the consumers.
Example: Various kinds of food and beverages may harm consumers and businessman could be covered against such harm.
The insurance market in Sri Lanka consists of Sri Lanka Insurance Board, Insurance companies, Insurance brokers and Insurance agents.
• The function of the Sri Lanka insurance board is established for the development of the insurance industry, responsibility of supervising and organize them in a systematic way.
The functions of the Sri Lanka Insurance board are given below. • Registration of insurance companies
• Registration of insurance brokers
• Cancellation of insurance companies
• Determine the limitation of funds that could be invested
• Consultation services rendered to the government in relation to organizing and developing the insurance industry.
• Implementation of government policies and programs regarding insurance
• Implementing CESS tax for the development of insurances activities in business.
• Insurance companies mean companies established with the object of establishing insurance service to business activities and registered under the Act. No. 43 of 2003
• The insurance broker’s job is playing a role as middlemen to the insurer and the insuree regarding insurance and reinsurance and to obtain the possible policy for the client. Insurance brokers are registered and they expect brokerage or commission for the job they do.
• A person whose aim is to receive commodation for the function he renders.
• The insurance companies that undertake the liability of the insured have an insurable interest over the subject matter insured or an insurance company will take part of risk insured with another companies called reinsurance.
• The advantages of reinsurance is that it covers the heavy liability by spreading the risk in order to reduce the commitments made by the insurer to an average amount.
• The following are the benefits received by the insurer in re- insurance.
• By reinsurance the liability of the insurance companies can be spread among many companies and by that the premium that is charges by each insurance company can be maintained at a low level.
• There is a stable existence and firmness, to claim coverage if damage occurs to a large property that had been insured.
The following are the classification of financial institutions in Sri Lanka
• The Central Bank of Sri Lanka
• Banking Sector
• Licensed commercial banks
• Licensed specialized banks
• Other institutions which accept deposits
• Registered finance companies
• Co-operative rural banks
• Thrift and credit co-operative societies (Sanasa)
• Other financial institutions
• Specialized leasing companies
• Vanik/ Merchant banks
• Primary dealers
• Share brokers companies
• Unit trusts
• Venture capital companies
• Credit rating organizations
• Contractual saving institutions
• Insurance companies
• Employees trust fund
• Employees provident fund
• Approved private provident fund
• Government service provident fund (According to Central Bank annual report- 2008)
• The financial organizations which accepts current account, savings account and other deposits, operates foreign exchange activities and are able to create money are called licensed commercial banks.
• There are large numbers of licensed commercial banks registered under the Central Bank of Sri lanka. A few banks are owned by the government sector whereas the majority of the banks are owned by the private sector.
• Licensed commercial banks provide various services including acceptance of deposits and lending money.
• Give more clear information to the students about the various services which make business activities easier.
• Licensed specialized banks can be defined as follows. Licenced specialized banks are the financial institutions which have obtained a license from the Central Bank to conduct specialized banking business under the banking act. These banks are not permitted to maintain current accounts or foreign exchange transactions. These are special characteristics of the licensed specialized banks. However, they are authorized to accept savings and time deposits.
• Explain clearly the importance of such services including accepting deposits and lending money to business by the licensed specialized banks
of such services including accepting deposits and lending money to business by the licensed specialized banks
• Suggest examples of licenced specialized banks.
• The following is the description of registered finance companies. • A public limited company which is registered under the Financial Companies Act and obtains a license from the Central Bank of Sri Lanka.
The following functions are performed by finance companies
• Financing on hire purchase
• Trading on real estate
• Provision of leasing facilities
• Providing short term loans
term loans
• Investing money on government securities, treasury bonds
on government securities, treasury bonds
• Acceptance of term deposits
• Describe the contribution rendered by the above functions for the performance and the growth of businesses
• Mention a few examples of registered finance companies.
The various functions carried out by the cooperative rural banks are as follows
• Accepting both deposits of members as well as non- members.
• Providing pawning facilities
• Acceptance of different categories of deposits. (Savings and to Fixed deposits )
• Providing loans to its members for the purpose of agriculture, production, Industries and trade.
• Disseminate the co-operative life-style among rural people
• Thrift and credit cooperative society (Sanasa) gives a helping hand to business activities
• Basic objectives of the society is promoting saving habits and providing loans to members. It should obtain a license from the commissioner of cooperatives under the co-operative act. It accepts money as savings and shares from members and provides loans to members.
• Leasing companies could be defined as follows: A special financial institution which provides money for businessmen in order to lease equipment or any other asset and is known as a leasing company. The main income of these leasing companies is the normal rent, received by giving the particular movable assets on lease.\
or any other asset and is known as a leasing company. The main income of these leasing companies is the normal rent, received by giving the particular movable assets on lease.\
Advantages gained by a businessman from leasing companies are as follows
• Arranging facilities for the use of valuable assets without paying the whole value.
• Exemption from income tax for the payment of rent on lease.
• Helps eliminate capital risks as well as losses incurred due to outdated machines.
• Is not shown on the liability side of the balance sheet of the business.
• Earning a high income without investing a large amount of money
• Indicates examples of leasing companies
• A stock brokers company acts as an intermediate person for the purchase or sale of stocks and debentures from incorporated companies
acts as an intermediate person for the purchase or sale of stocks and debentures from incorporated companies
The following are the commercial services carried out by stock broker companies
• Accept sales or purchase orders from investors.
• Open up an account for investors at the central depositary system.
• Provide necessary advice to invest in shares and debentures.
• Confirm maximum advantages that could be obtained by the investors by analyzing the sharemarketand by preparing a report on market research.
• Give approval to listed companies after they have fulfilled the necessary requirements.
• Help capital formation at the public companies
• Present examples of share brokers companies .
.
• The special financial institutions which are specialized in providing management and consultancy services are called merchant banks. They do not accept deposits.
Merchant banks provide various services to businessmen.
• Preparing project reports
• Providing consultancy services for finance and marketing
• Performing underwriting services
• Providing leasing services
• Give examples of merchant banks.
• Introduce unit trustees in the following manner.
• Unit trusts mobilize resources by selling its units to the investors and invests funds through the stock exchange. Funds are invested in the investment portfolio by professional investment managers. The benefits of the unit trust are distributed among the unit holders.
There are three parties included in a unit trust.
• Trustees
• Fund management companies
• Unit holders or investors
• The following are the advantages of investing in a unit trust
• Risking money in various investments will be minimized through a unit trust.
• Obtain services from professional managers on investing.
• Venture capital companies: Provide funds to start new business activities, expand present
business activities, purchase or take over business activities. In addition to that it provides
under writing services and syndicate of credit.
• Mention examples of venture capital
• Credit rating organizations provide services to businesses.
• Provision of guidance to investors to identity the features of financial instruments in
in
the finance market. This helps to evaluate the financial strength of creditors and to
compare them without difficulty in an international grade as there are common criteria
being used for the credit rating.
Contractual saving institutions also provide services to business.
• Insurance company
These organizations obtain funds by providing various insurance policies. Insurance
companies invest in the financial market. Insurance policies are issued to entrepreneurs
to cover their various risks.
• Employees provident fund and pensions schemes
• These schemes are constituted under labour law. This fund is formed with the
contributions from both the parties. The contributed money with benefits would be
given to the employees at the time of their retirement.
Money is anything which is acceptable in common in exchange for goods or services
• The evaluation of money could be listed out from the time of the barter system to the present day. • Use of commodities : Stones, Shells, bones of animals, tobacco.
• Use of metal contents: Some metal contents such as gold, Sliver were circulated
• Use of metallic coins: Face value and the material value indicated on the metallic coins
• Use of notes and coins: In order to avoid problems, currency notes and coins were published by the authorized government institution.
Example:-
Sri Lanka – Rupee, Cent
United kingdom – Sterling pounds, Penny
United states of America – Dollar, Cent
Countries of the European Community – Euro, Cent
• Use of Bank money
Cheques being used through current accounts
• Uses of electronic money
money
There is electronic money, special cards were introduced through the development of information and digital technology.
money, special cards were introduced through the development of information and digital technology.
Eg. Credit card, Debit card, Prepaid card
Characteristics of good money stated as follows
• Acceptability – People should accept commonly
• Durability – Money needs to be long – lasting
• Scarcity – The commodity used must have a stable value and be scarce in nature
• Portability – Money should be easy to handle.
• Money should be easy to recognize
• Divisibility – The money used has to be capable of being divided into units
The money used at present can be categorized as follows
• Currency – Notes and coins issued by an authorized body is called currency. This has to be accepted legally..
• Bank money:
This refers to the amount of money which represents the demand deposits or the current
account balances maintained at commercial banks. These balances at banks are being
used to issue cheques. This has less liquidity when compared to currency but high
liquidity than near money.
• Near Money :
Though these are lower in liquidity than currency, it is easily and quickly convertible
into cash
Example:
Savings and fixed deposits in commercial banks, commercial papers, treasury bills
• Electronic Money (E-Money):
Money (E-Money):
A type of money being invented as a result of information technology and digital
technology which is used nationally and internationally.
Example:
• Debit Card :
A Bank account is necessary to obtain a debit card and debit card transactions are
carried out automatically through an electronic network.
network.
• Credit card :
A Bank account is not necessary to obtain a credit card, Goods and services can be
bought up to a certain value using a credit card.
• Prepaid card :
This card could be obtained by paying money in advance.
The following are some facilities when using these cards while settling payments
• ATM – Automated Teller Machines
• EFTPOS – Electronic Funds Transfer Point of Sales
• Tele banking – Tele banking facilities
• On line banking – Internet Banking Services