Diversity of respiratory structures in the animal kingdom.
- The area where gaseous exchange takes place with the environment is called the respiratory surface.
- Gaseous exchange takes place in all organisms by the physical process of diffusion. So the respiratory surfaces must have the following properties.
- It must be permeable to respiratory gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- It must be moist/wet. Because dissolved oxygen will diffuse through the respiratory surface.
- It must be thin, short distance, therefore diffusion will be efficient.
- It must possess a large area to allow sufficient volume gases to be exchanged according to organisms need.
- It should possess good supply of blood .because blood will remove oxygen from the respiratory surface thus maintaining oxygen concentration gradient.
- There is a huge diversity in respiratory organs in the animal kingdom.
- Organisms require oxygen either direct from the atmosphere or from the dissolved O2 in water.
- There are number of differences in the O2 content in the air and water.
- Atmosphere-21%
- Water-0.8%
Generalized structure of human alimentary canal 
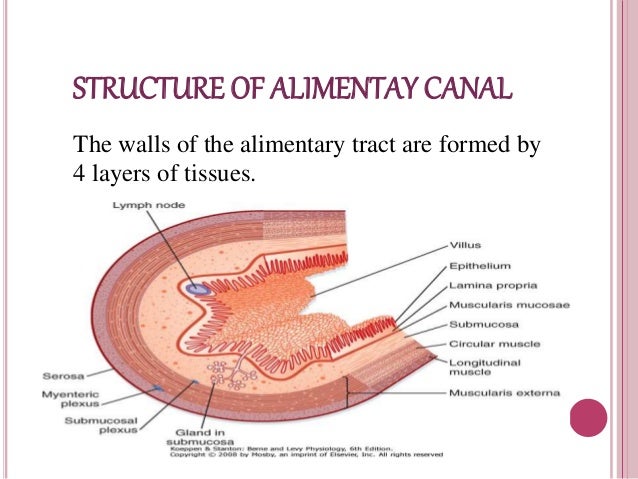
- The structure of the alimentary canal follows a consistent pattern from the level of oesophagus onwards
- Modification from the general plan is due to the special function associated with those organs
- The wall of the alimentary tract is formed by 4 layers in sequence from outside as follows
- Serosa/ Adventita
- Muscularis Externa
- Sub Mucosa
- Mucosa
- Major variation from the basic plan occurs generally in the mucosa
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Absorption of nutrients
Absorption of nutrients
- Absorption of end products of the digestion occurs mainly in the small intestine.
- By 3 main process
1) Diffusion
2) Facilitated diffusion – ATP is not required
3) Active transport – ATP is used
- Carbohydrate as disaccharide and protein as dipeptide and tripeptide are actively transported into the microvilli and the digestion is completed within the enterocytes.
- Carbohydrates as monosaccharides, protein as amino acid and fat as fatty acid and glycerol are absorbed into the enterocytes.
- Monosaccharide, amino acid, water soluble vitamins, minerals and water are absorbed into the blood capillaries in the villi.
- Some proteins such as antibodies in the mother’s milk are absorbed unchanged.
- Fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed and synthesized as triglycerides within the enterocytes.
- The triglycerides are absorbed into the lacteal. Fat soluble vitamins also absorbed along with the triglycerides.
Balance diet
- A diet containing essential nutrients, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, dietary fibers, minerals, vitamins and water in the correct proportion is called as a balanced diet.
- A balanced diet is essential for health, if any nutrient is eaten in excess or is deficient, health may be adversely affected
Dietary fibers
- Fiber is not a nutrient as it is not digested or absorbed, but it has many beneficial effects on the digestive tracts.
1) Provides bulk to the diet and helps to satisfy the appetite
2) Stimulates peristalsis
3) Attracts water, increasing bulk and softness of faecus
4) Increases frequency of defecation, preventing constipation
- Prevents some gastrointestinal disorders
Example: – Colo-rectal cancer
Disorders in the alimentary canal
- Gastritis
- When there is an excess of acid in the stomach causing damages to the mucosa.
- Due to the damages, blisters are formed.
- The causes of short-term gastritis are 1) Mental stress or tension
2) Prolonged starvation
3) Consumption of alcohol
4) Suffering from some diseases such as tuberculosis, syphilis etc.
5) Prolonged use of aspirin
- Chronic or long-term gastritis also associated with the bacteria called Helicobacter pylori
- Constipation
- Inhibition of the reflex action in defecation may lead to constipation.
- Constipation causes pain of the anus and difficulties in defecating.
Control
- Behavioral adjustment should be developed to carry out defecation.
- Adequate fibers in the diet.


 Absorption of nutrients
Absorption of nutrients